PDF) Identification of de novo EP300 and PLAU variants in a patient with Rubinstein–Taybi syndrome-related arterial vasculopathy and skeletal anomaly
Por um escritor misterioso
Last updated 22 dezembro 2024
COL4A2 mutation associated with familial porencephaly and small-vessel disease
De novo variation in EP300 gene cause Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome 2 in a Chinese family with severe early-onset high myopia, BMC Medical Genomics
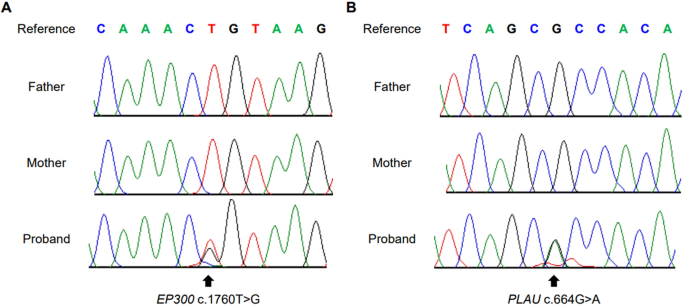
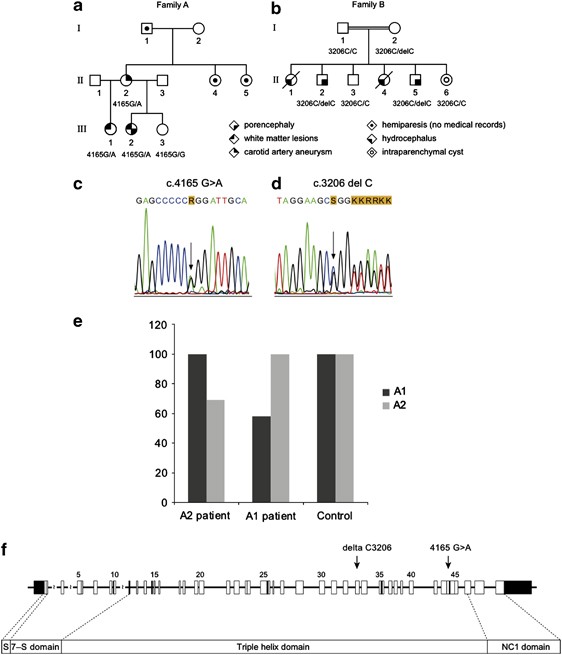
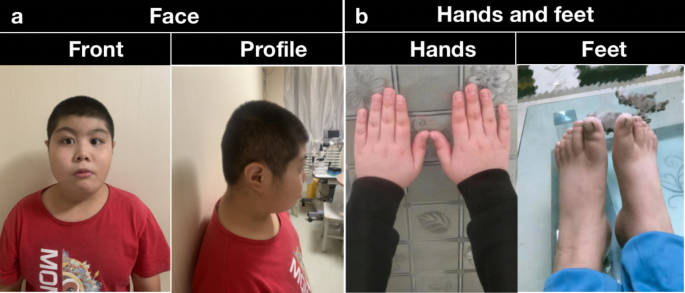
Identification of de novo EP300 and PLAU variants in a patient with Rubinstein–Taybi syndrome-related arterial vasculopathy and skeletal anomaly
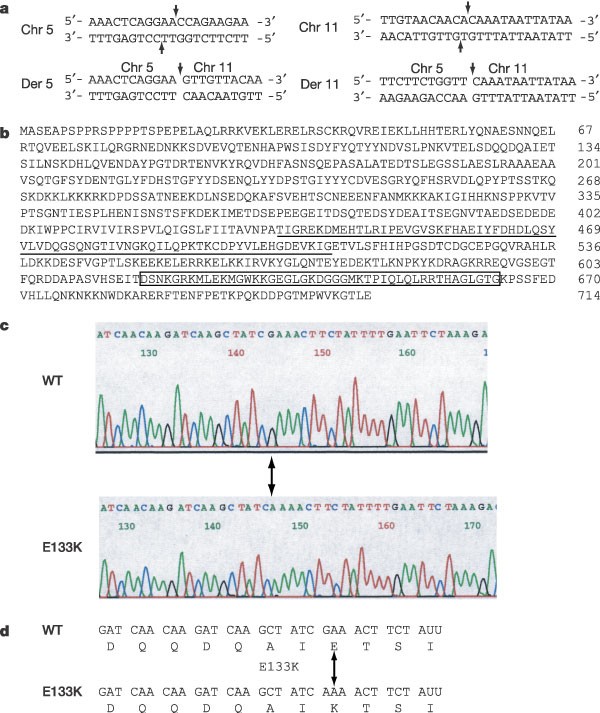
Identification of an angiogenic factor that when mutated causes susceptibility to Klippel–Trenaunay syndrome

Further delineation of an entity caused by CREBBP and EP300 mutations but not resembling Rubinstein–Taybi syndrome - Menke - 2018 - American Journal of Medical Genetics Part A - Wiley Online Library
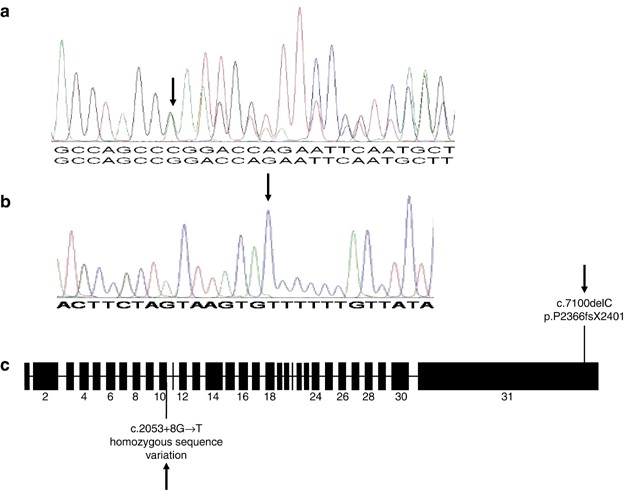
Confirmation of EP300 gene mutations as a rare cause of Rubinstein–Taybi syndrome
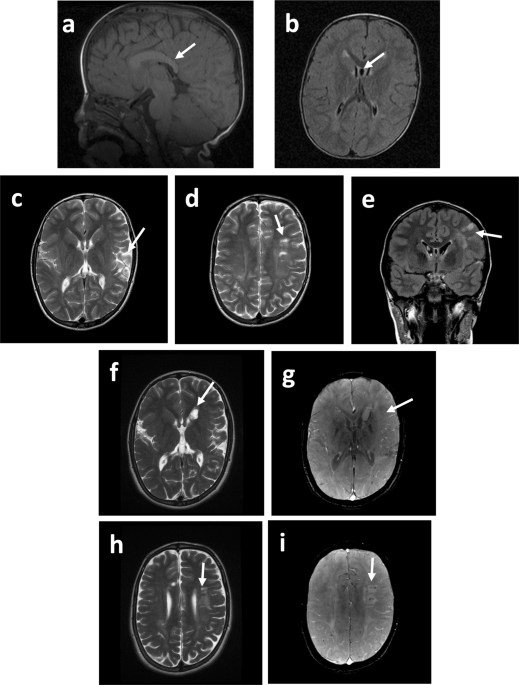
A novel de novo MTOR gain-of-function variant in a patient with Smith-Kingsmore syndrome and Antiphospholipid syndrome
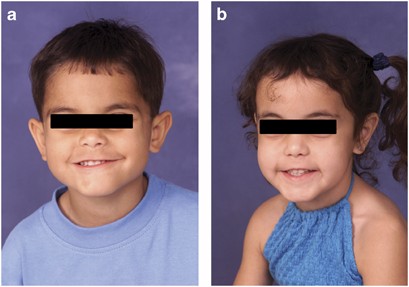
Mutations in COL27A1 cause Steel syndrome and suggest a founder mutation effect in the Puerto Rican population

PDF) Identification of de novo EP300 and PLAU variants in a patient with Rubinstein–Taybi syndrome-related arterial vasculopathy and skeletal anomaly
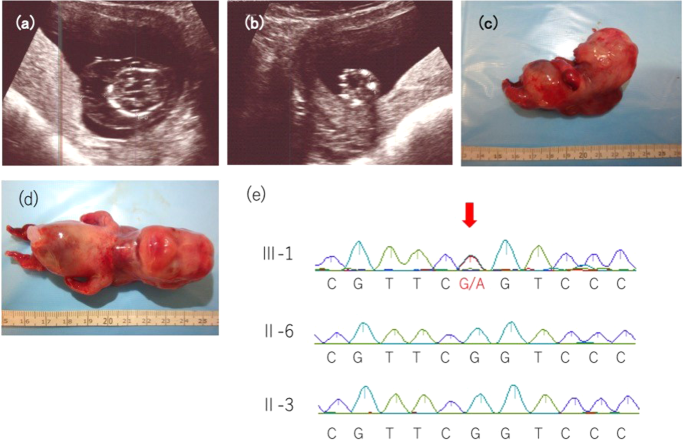
Novel missense COL2A1 variant in a fetus with achondrogenesis type II

Urokinase-Type Plasminogen Activator Deficiency in Bone Marrow–Derived Cells Augments Rupture of Angiotensin II–Induced Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms

Genetic Basis for Congenital Heart Disease: Revisited: A Scientific Statement From the American Heart Association
Recomendado para você
-
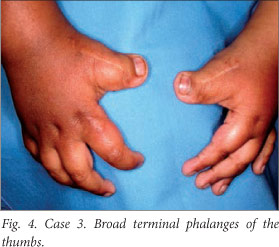 Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome: Dental manifestations and management22 dezembro 2024
Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome: Dental manifestations and management22 dezembro 2024 -
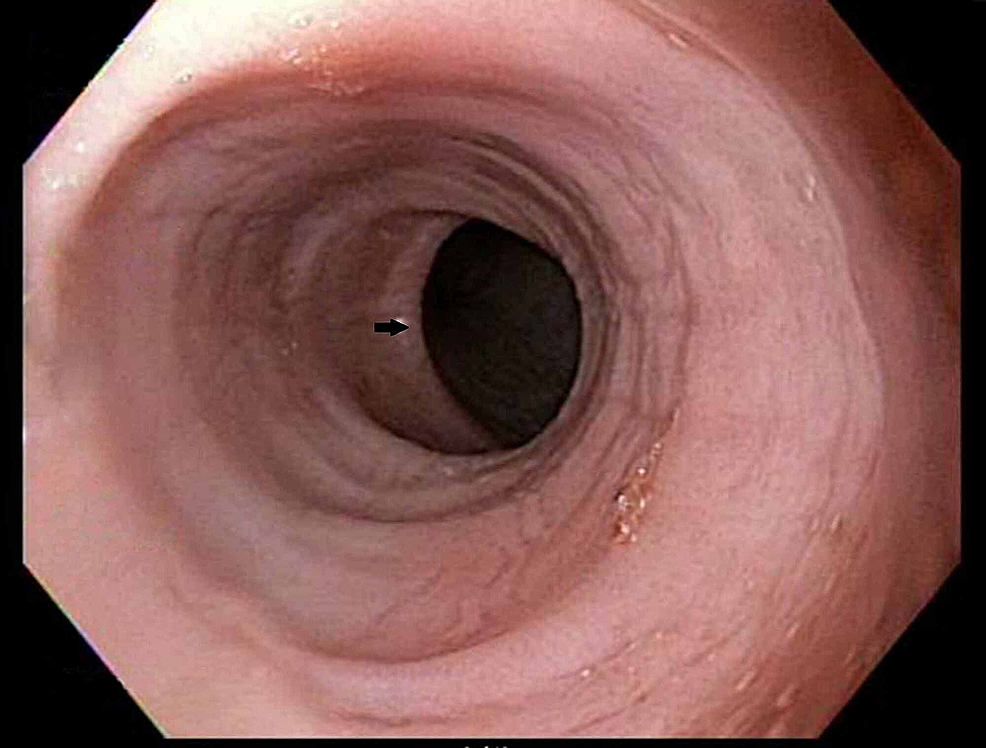 Cureus Barrett's Esophagus in Rubinstein-Taybi Syndrome22 dezembro 2024
Cureus Barrett's Esophagus in Rubinstein-Taybi Syndrome22 dezembro 2024 -
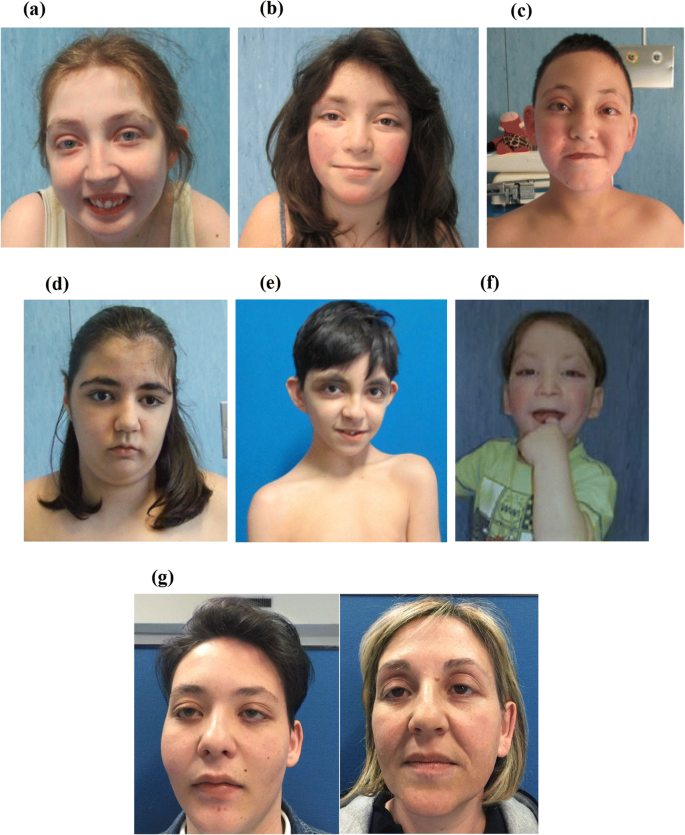 Clinical heterogeneity of Kabuki syndrome in a cohort of Italian patients and review of the literature22 dezembro 2024
Clinical heterogeneity of Kabuki syndrome in a cohort of Italian patients and review of the literature22 dezembro 2024 -
 Cornelia de Lange Syndrome - GeneReviews® - NCBI Bookshelf22 dezembro 2024
Cornelia de Lange Syndrome - GeneReviews® - NCBI Bookshelf22 dezembro 2024 -
 PDF) An unusual presentation of Rubinstein-Taybi Syndrome with bilateral postaxial polydactyly Corresponding author22 dezembro 2024
PDF) An unusual presentation of Rubinstein-Taybi Syndrome with bilateral postaxial polydactyly Corresponding author22 dezembro 2024 -
 Full article: Psychomotor, cognitive, and socio-emotional developmental profiles of children with Rubinstein-Taybi Syndrome and a severe intellectual disability22 dezembro 2024
Full article: Psychomotor, cognitive, and socio-emotional developmental profiles of children with Rubinstein-Taybi Syndrome and a severe intellectual disability22 dezembro 2024 -
 Somatic and germ‐line mosaicism in Rubinstein–Taybi syndrome - Chiang - 2009 - American Journal of Medical Genetics Part A - Wiley Online Library22 dezembro 2024
Somatic and germ‐line mosaicism in Rubinstein–Taybi syndrome - Chiang - 2009 - American Journal of Medical Genetics Part A - Wiley Online Library22 dezembro 2024 -
 Rubinstein–Taybi syndrome in diverse populations - Tekendo‐Ngongang - 2020 - American Journal of Medical Genetics Part A - Wiley Online Library22 dezembro 2024
Rubinstein–Taybi syndrome in diverse populations - Tekendo‐Ngongang - 2020 - American Journal of Medical Genetics Part A - Wiley Online Library22 dezembro 2024 -
 Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome with agenesis of corpus callosum. - Abstract - Europe PMC22 dezembro 2024
Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome with agenesis of corpus callosum. - Abstract - Europe PMC22 dezembro 2024 -
 Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome with agenesis of corpus callosum22 dezembro 2024
Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome with agenesis of corpus callosum22 dezembro 2024
você pode gostar
-
 Demon Slayer (Kimetsu no Yaiba) Discussion Thread #222 dezembro 2024
Demon Slayer (Kimetsu no Yaiba) Discussion Thread #222 dezembro 2024 -
 Sonic Rush 3D em COQUINHOS22 dezembro 2024
Sonic Rush 3D em COQUINHOS22 dezembro 2024 -
 10 Richest People in the World22 dezembro 2024
10 Richest People in the World22 dezembro 2024 -
 where to watch the owl house episode 2|TikTok Search22 dezembro 2024
where to watch the owl house episode 2|TikTok Search22 dezembro 2024 -
Rowena Posters and Art Prints for Sale22 dezembro 2024
-
 5 gatos mais famosos dos filmes e desenhos (parte 1)22 dezembro 2024
5 gatos mais famosos dos filmes e desenhos (parte 1)22 dezembro 2024 -
 Confira Últimas Notícias Sobre Animes - Anime United22 dezembro 2024
Confira Últimas Notícias Sobre Animes - Anime United22 dezembro 2024 -
 Catskills & Adirondacks - Planning Your Winter Mountain Getaway22 dezembro 2024
Catskills & Adirondacks - Planning Your Winter Mountain Getaway22 dezembro 2024 -
 FromSoftware Thanks Fans for Elden Ring Support, But Offers No New22 dezembro 2024
FromSoftware Thanks Fans for Elden Ring Support, But Offers No New22 dezembro 2024 -
 Horcus on X: Pearl Harbor 2022 (Valorant Edition) 😂 / X22 dezembro 2024
Horcus on X: Pearl Harbor 2022 (Valorant Edition) 😂 / X22 dezembro 2024