Retrospective evaluation of labetalol as antihypertensive agent in
Por um escritor misterioso
Last updated 19 setembro 2024
Background To evaluate the effect on arterial blood pressure (ABP) of labetalol infusion as treatment for perioperative non nociceptive acute hypertension in dogs. The clinical records of dogs receiving intra or postoperative labetalol infusion were retrospectively reviewed. Invasive systolic (SAP), mean (MAP) and diastolic (DAP) arterial pressure and heart rate (HR) before labetalol infusion (T0) and 15, 30, 45 and 60 min (T1, T2, T3 and T4 respectively) after infusion were retrieved. The dose rate of labetalol infusion and use of concurrently administered drugs that could have potentially affected ABP and/or HR were also recorded. ANOVA for repeated measures and Dunnett’s multiple comparison test were used to determine the effect of labetalol on ABP and HR. Differences were considered significant when p < 0.05. Results A total of 20 dogs met the inclusion criteria, and hypertension was documented after craniotomy (12/20), adrenalectomy (4/20) and other procedures (4/20). Five dogs received labetalol intraoperatively, 14 postoperatively, and 1 during the surgical procedure and recovery. Median infusion duration and rate were 463 (60-2120) minutes and 1.1 (0.2–3.4) mg/kg/h respectively. Median loading dose was 0.2 (0.2–0.4) mg/kg. Labetalol produced a significant decrease in SAP and DAP at all time points compared to T0 (p < 0.05), while the effect was not significant at T1 for MAP (p = 0.0519). Median maximum MAP decrease was 31 (20–90) mmHg. Heart rate did not increase significantly during treatment (p = 0.2454). Acepromazine given before or during labetalol treatment did not reduce significantly ABP (p = 0.735). Conclusions Labetalol produced a reliable and titratable decrease in ABP with non significant increase in HR.

IV labetalol and oral nifedipine in acute control of severe hypertension in pregnancy–A randomized controlled trial - ScienceDirect
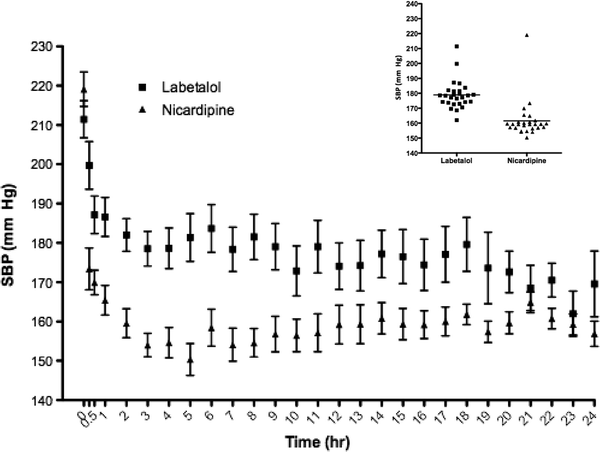
A Prospective Evaluation of Labetalol Versus Nicardipine for Blood Pressure Management in Patients with Acute Stroke
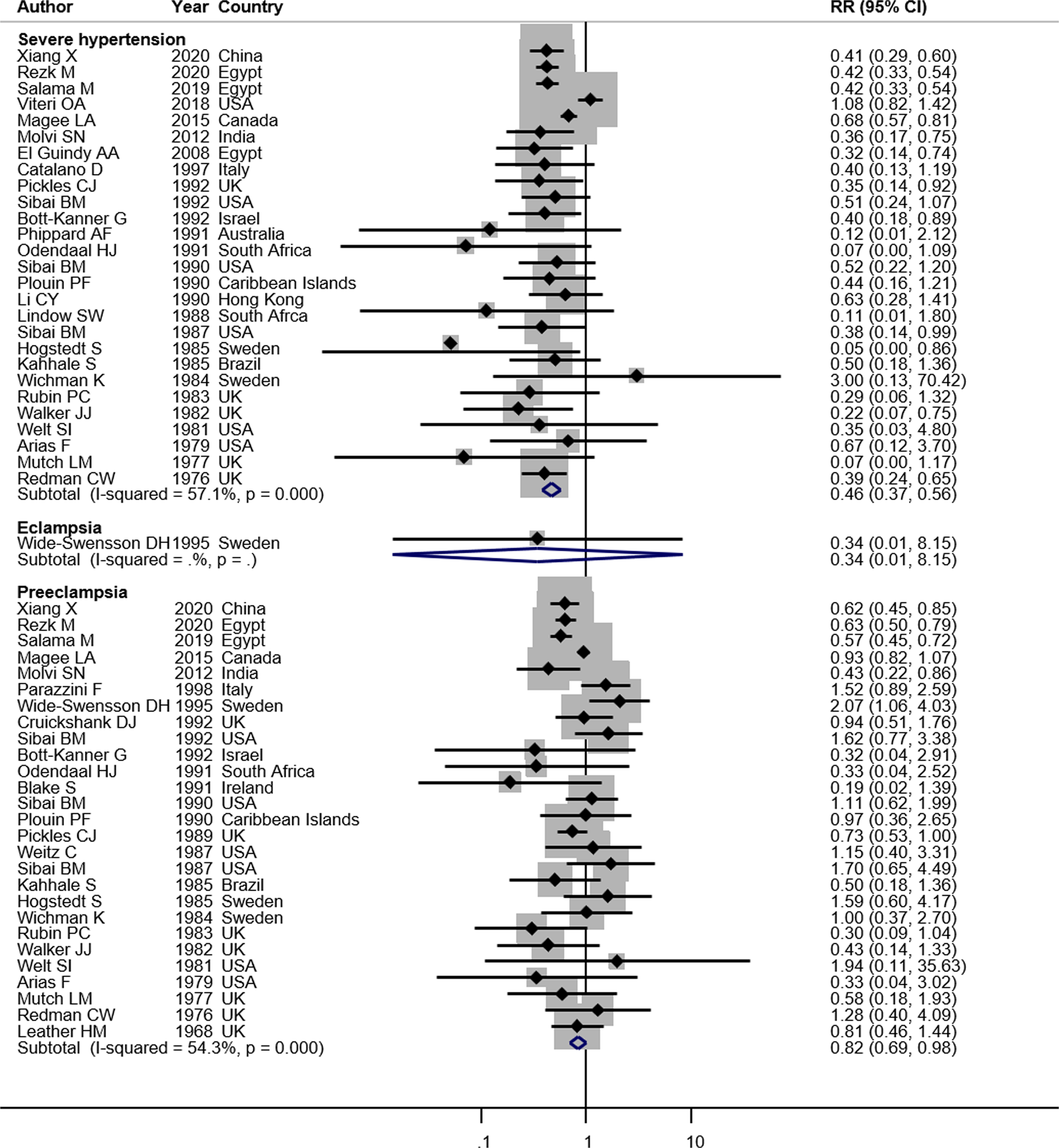
Optimal blood pressure target to prevent severe hypertension in pregnancy: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Comparison of labetalol with other anti-hypertensive drugs. - Abstract - Europe PMC

Management of Hypertension on the Labor and Delivery Unit: Delivering Care in the Era of Protocols and Algorithms
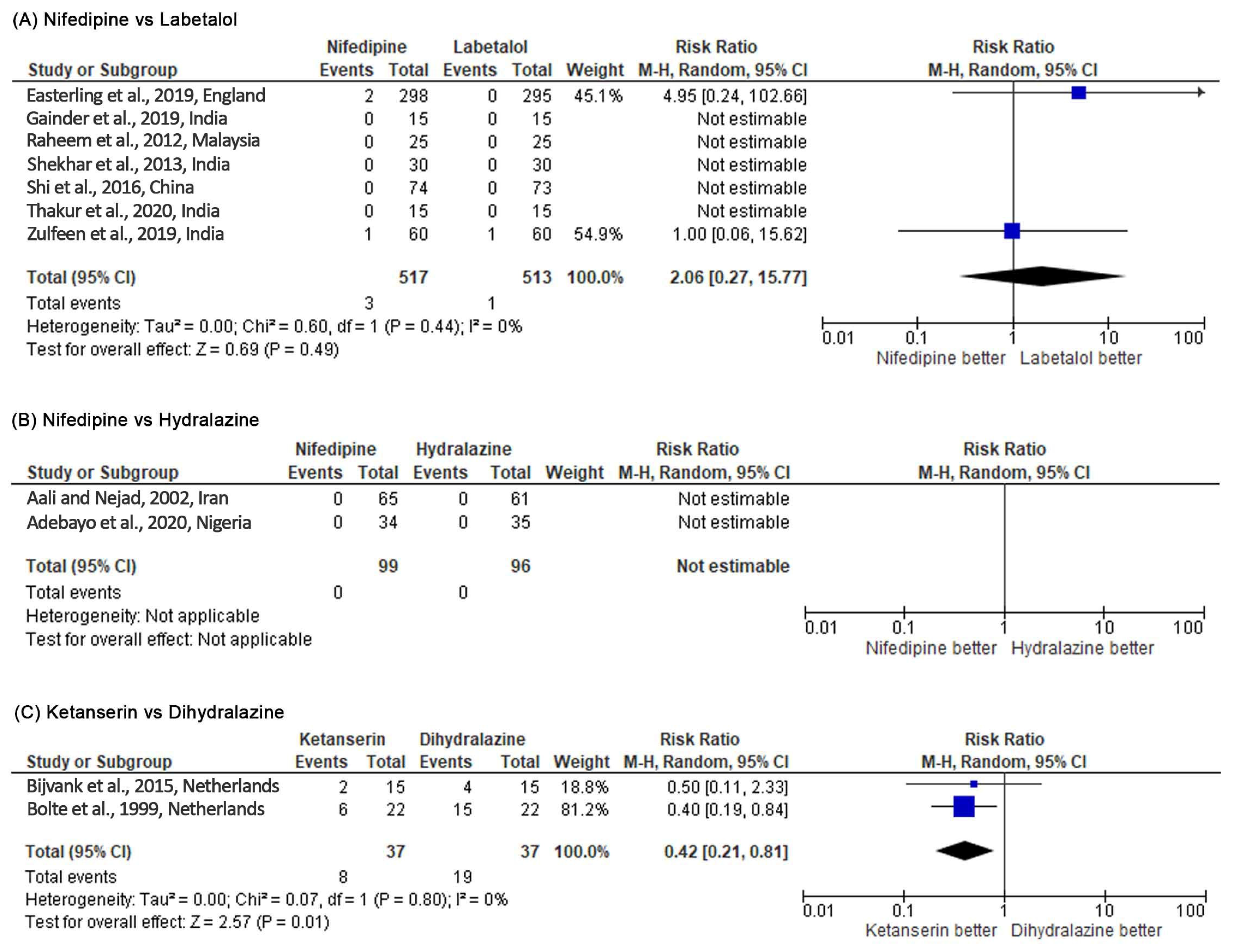
Healthcare, Free Full-Text
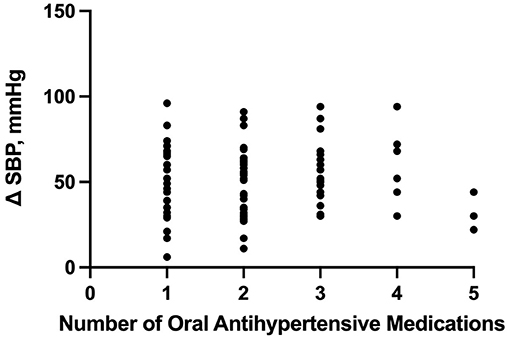
Frontiers Systolic Blood Pressure Variability When Transitioning From Intravenous to Enteral Antihypertensive Agents in Patients With Hemorrhagic Strokes

Oral nifedipine versus intravenous labetalol in hypertensive urgencies and emergencies of pregnancy: a randomized clinical trial - B Sathya Lakshmi, Papa Dasari, 2012

Retrospective review of the use of as-needed hydralazine and labetalol for the treatment of acute hypertension in hospitalized medicine patients
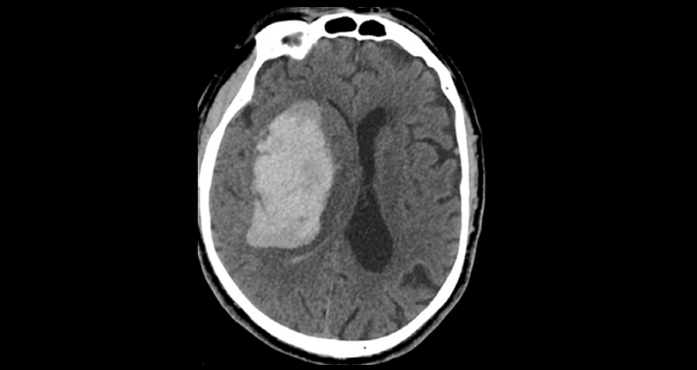
Blood Pressure Control With Labetalol Fails to Decrease Infection Risk in Intracerebral Hemorrhage - Neurovascular Exchange
Recomendado para você
-
 LABETALOL HYDROCHLORIDE tablet, film coated19 setembro 2024
LABETALOL HYDROCHLORIDE tablet, film coated19 setembro 2024 -
 Labetalol Injection 100mg Labil, Rizochem Pharmaceuticals, Exporter19 setembro 2024
Labetalol Injection 100mg Labil, Rizochem Pharmaceuticals, Exporter19 setembro 2024 -
Anesthesia information - Lebetalol19 setembro 2024
-
 EFFECTIVENESS OF LABETALOL FOR STRESS ATTENUATION IN MODIFIED ECT19 setembro 2024
EFFECTIVENESS OF LABETALOL FOR STRESS ATTENUATION IN MODIFIED ECT19 setembro 2024 -
Use of labetalol and methyldopa in pregnancy-induced hypertension19 setembro 2024
-
 Labeheal Labetalol HCL Injection IP, Healing Pharma India Pvt. Ltd19 setembro 2024
Labeheal Labetalol HCL Injection IP, Healing Pharma India Pvt. Ltd19 setembro 2024 -
 Labetalol Injection: Benefits, Uses, Price, and Side Effects19 setembro 2024
Labetalol Injection: Benefits, Uses, Price, and Side Effects19 setembro 2024 -
 Labetalol 100mg Tablet Labigest, Exporter, Supplier19 setembro 2024
Labetalol 100mg Tablet Labigest, Exporter, Supplier19 setembro 2024 -
 Healthy Transitions COMMON SIDE EFFECTS AND DRUG INTERACTIONS19 setembro 2024
Healthy Transitions COMMON SIDE EFFECTS AND DRUG INTERACTIONS19 setembro 2024 -
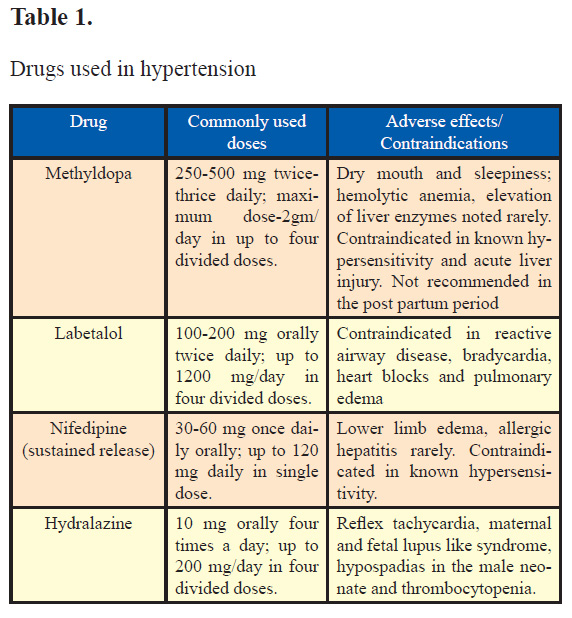 Hypertension in Pregnancy: Current Perspective19 setembro 2024
Hypertension in Pregnancy: Current Perspective19 setembro 2024
você pode gostar
-
 Tails doll curse (UCN mod) by dr_2401 - Game Jolt19 setembro 2024
Tails doll curse (UCN mod) by dr_2401 - Game Jolt19 setembro 2024 -
 16.600+ Boca Aberta Ilustrações fotos de stock, imagens e fotos19 setembro 2024
16.600+ Boca Aberta Ilustrações fotos de stock, imagens e fotos19 setembro 2024 -
 Rewatching Bleach just caught this - Does that mean that if19 setembro 2024
Rewatching Bleach just caught this - Does that mean that if19 setembro 2024 -
 Super Mario Bros. O Filme Direct – 09/03/2023 (Trailer Final) - Cobertura em português19 setembro 2024
Super Mario Bros. O Filme Direct – 09/03/2023 (Trailer Final) - Cobertura em português19 setembro 2024 -
 Portugal map freehand drawing on white background. 6563989 Vector Art at Vecteezy19 setembro 2024
Portugal map freehand drawing on white background. 6563989 Vector Art at Vecteezy19 setembro 2024 -
 Molde Capacete do Anime Chainsaw Man - Cosplay19 setembro 2024
Molde Capacete do Anime Chainsaw Man - Cosplay19 setembro 2024 -
 Review - Microsoft Flight Simulator (Xbox Series S/X)19 setembro 2024
Review - Microsoft Flight Simulator (Xbox Series S/X)19 setembro 2024 -
Steam Community :: Chessmaster19 setembro 2024
-
 RAINBOW FRIENDS CHAPTER 2 COLORING PAGES / COLOR ALL NEW MONSTERS RAINBOW FRIENDS 219 setembro 2024
RAINBOW FRIENDS CHAPTER 2 COLORING PAGES / COLOR ALL NEW MONSTERS RAINBOW FRIENDS 219 setembro 2024 -
 block dash infinito stumble guys 0.40 apk19 setembro 2024
block dash infinito stumble guys 0.40 apk19 setembro 2024